Installation
serversideup/php is compatible with any container orchestrator that supports Docker images (Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, Docker Compose, HashiCorp Nomad, etc.). All images are hosted on DockerHub and GitHub Packages for free. Containers default to running Debian, but Alpine images are also available.
Quick Start
In order to run containers, we need a container engine installed such as Docker. You can follow Docker's installation guide to get started. Confirm Docker is working by running these commands in your terminal:
# Check Docker version
docker --version
# Check Docker Compose version
docker compose version
If you see version numbers after running the commands, you're ready to go!
Create a new sample project
Let's create a new sample project to test our Docker setup. Open up your terminal and run the following commands:
# Create a project directory with a public directory
mkdir -p my-php-project/public
# Change directory to our project
cd my-php-project
Once we're in our project directory, we will want to create two files:
public/index.php- The file that will be served when someone visits our sitecompose.yml- The place where we will put our configuration files
The content of these files should look like:
<?php
// Let's just print out some PHP info
phpinfo();
?>
Save these files and ensure they are in the exact structure above.
Bringing up your PHP app
From your project root directory, run the following command to start your PHP app:
my-php-project). If you do not have compose.yml in the same directory as you run this command, the command will not work. Also, make sure you don't have any other containers or services that are currently running on port 80. If you do, you will need to stop them before running the following command.Start the PHP container
docker compose up
You'll see the logs appear in your terminal. Keep your terminal open as we'll need it to control the container.
Viewing your PHP app
To view your PHP app, open your browser and navigate to http://localhost. You should see the PHP info page showing PHP 8.3 with the fpm-nginx variation:
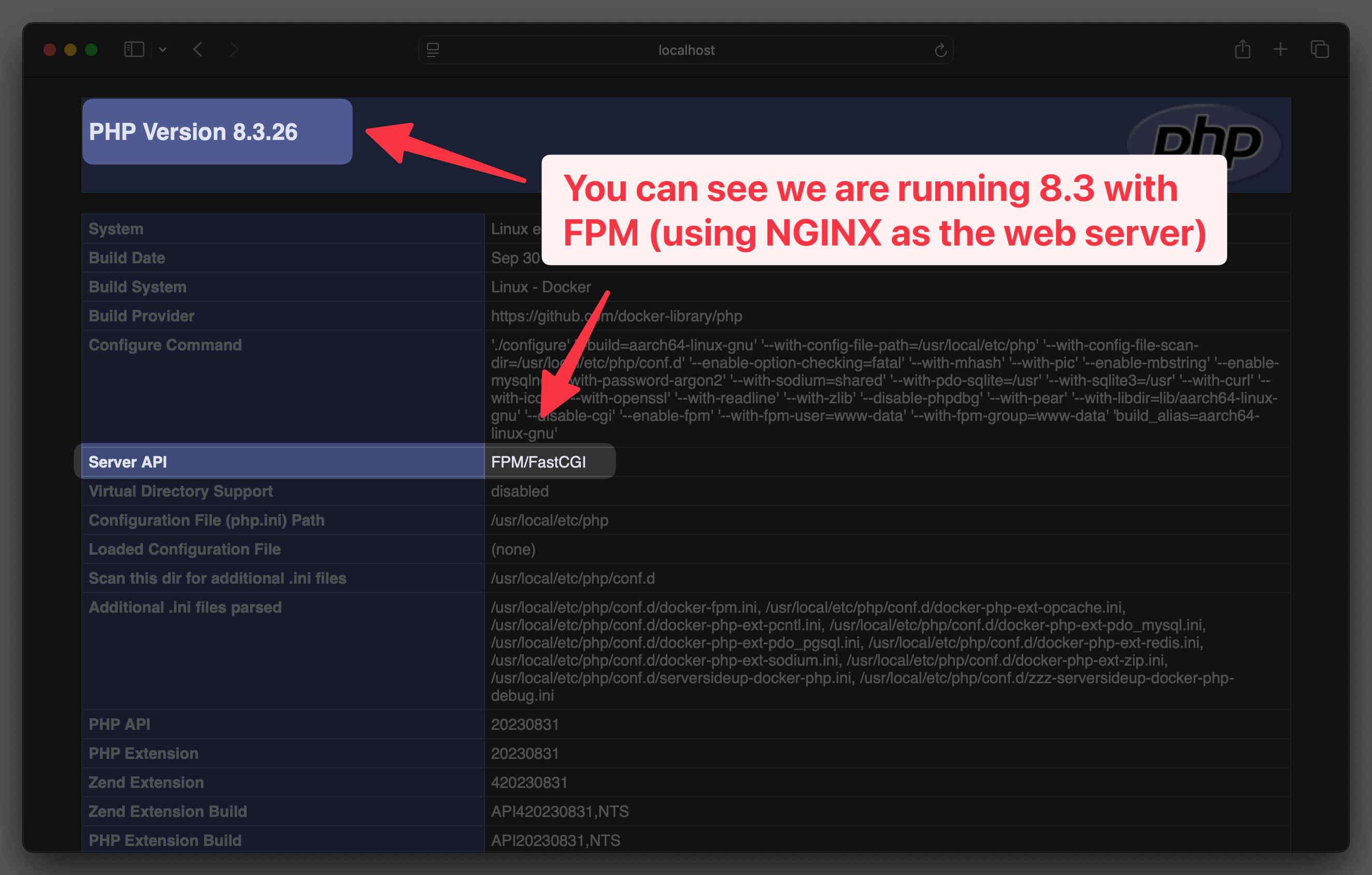
You can see the PHP version is in the upper left corner of the page. But what's also cool is you can see the settings we configured in the compose.yml file are being applied.
Look for these values in the PHP info page:
upload_max_filesize- This should show250Mopcache.enable- This should showOff
Making changes
Let's make some upgrades to our PHP app:
- Let's upgrade to PHP 8.4
- Let's use FrankenPHP instead of FPM-NGINX
- Turn on OPCache
- Increase the upload limit to 500M
To do this, we need to need to:
Stop the container
Press + C on the original terminal window or you can run the following command in a new terminal window from your project root directory:
docker compose down
Making changes to your PHP app
Make the updates below to your compose.yml file:
services:
php:
# Change image to 8.4 with FrankenPHP
image: serversideup/php:8.4-frankenphp
ports:
- 80:8080
volumes:
- ./:/var/www/html
environment:
# Increase the upload limit to 500M
PHP_UPLOAD_MAX_FILE_SIZE: "500M"
# Turn OPCache on
PHP_OPCACHE_ENABLE: "1"
Bring the container up again
docker compose up
You'll see the logs appear in your terminal. Keep your terminal open as we'll need it to control the container.
Refresh your browser
Check http://localhost again and you should see the changes we made:

Holy smokes! We've upgraded to PHP 8.4 and you're using FrankenPHP! You can also find the changes to the PHP settings have been applied.

You've got this 💪
You've successfully created your first PHP app with Docker. Better yet, you've seen the power of serversideup/php where it's easy to change your PHP version and variation by changing a single line in your configuration file.
If you're curious what the whole process looks like from Development to Production, check out out guide below.
Learn how to deploy your PHP app from Development to Production