Configuring SSL
SSL encryption is natively supported in our images. With FrankenPHP, a trusted certificate can automatically be generated by Let's Encrypt. You can also bring your own certificates or have a self-signed certificate generated for you.
Supported Variations
SSL is natively supported in the following variations:
| Variation | SSL Support | Automated, Signed Certificate Support (via Let's Encrypt) |
|---|---|---|
cli | ❌ No | - |
fpm | ❌ No | - |
fpm-nginx | ✅ Yes | ❌ No (requires a reverse proxy in front of the container) |
fpm-apache | ✅ Yes | ❌ No (requires a reverse proxy in front of the container) |
frankenphp | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
SSL Modes
You can control SSL behavior with the SSL_MODE environment variable:
| SSL Mode | Description |
|---|---|
off (default) | HTTP only. |
mixed | HTTP and HTTPS. |
full | HTTPS only. HTTP requests will be redirected to HTTPS. |
Choose How to Run SSL in Production
You have a few options for running SSL in production:
| Approach | Certificate Type | Management Type | Zero-Downtime Deployments | Minimal Number of Containers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse Proxy (like Traefik or Caddy) | ✅ Trusted Certificate (via Let's Encrypt) | ✅ Automatic | ✅ Yes | ⚠️ 2 |
| FrankenPHP's built-in automatic HTTPS | ✅ Trusted Certificate (via Let's Encrypt) | ✅ Automatic | ❌ No | ✅ 1 |
| Bring Your Own Certificate | ✅ Trusted Certificate (through any vendor) | ❌ Manual | ❌ No | ✅ 1 |
| Self-signed | ❌ Self-signed Certificate | ✅ Automatic | ❌ No | ✅ 1 |
Reverse Proxy (recommended)
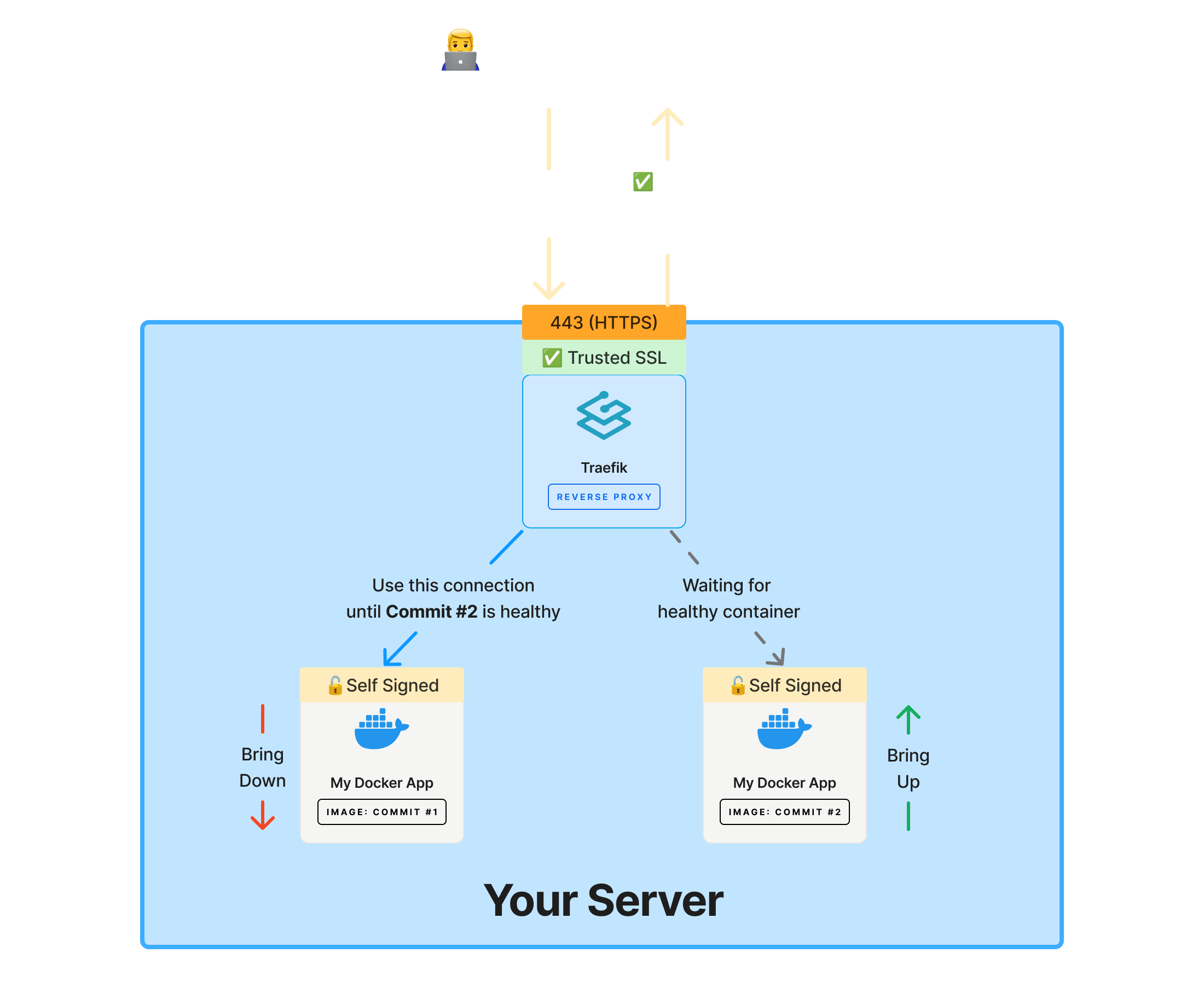 Our recommended approach is to use a reverse proxy like Traefik or Caddy that listens on ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS). The reverse proxy will forward traffic to your container on the non-privileged ports of 8080 (HTTP) or 8443 (HTTPS).
Our recommended approach is to use a reverse proxy like Traefik or Caddy that listens on ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS). The reverse proxy will forward traffic to your container on the non-privileged ports of 8080 (HTTP) or 8443 (HTTPS).
Using a reverse proxy unlocks two major benefits:
- Automatic SSL certificate management (via Let's Encrypt)
- Zero-downtime deployments
When you're running updates on containers, the reverse proxy stays online while updates are deployed to your containers in the background. Configuring a reverse proxy is outside the scope of this documentation, but you can reference the links below to learn more:
Use a Reverse Proxy When You Want...
- Zero-downtime deployments
- Automatic SSL certificate management (via Let's Encrypt)
- Load balancing
If you want a simple way to run your own reverse proxy with zero-downtime deployments, consider using Spin.
Learn more about SpinFrankenPHP's Built-in Automatic HTTPS
FrankenPHP provides automated HTTPS through Caddy. To directly expose FrankenPHP to the internet, you'll need to configure the following:
- Environment variables (for Caddy configuration)
- Ports (for direct exposure of ports 80 and 443)
- Volumes (for certificate files)
Environment Variables
Configure the following environment variables:
| Variable | Expected Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
CADDY_AUTO_HTTPS Default: "off" | on | Turn on Caddy's auto_https global directive. |
CADDY_HTTPS_SERVER_ADDRESS Default: "https://" | example.com or https://example.com | Set the server address for HTTPS. Pro tip: You can use $APP_URL from your .env file to set this value. |
SSL_MODE Default: "off" | full or mixed | Configure how Caddy handles HTTP and HTTPS requests. |
Ports
Configure the following ports:
| Ports to Publish | Description |
|---|---|
80 → 8080 | HTTP traffic will be proxied to the container on port 8080. |
443 → 8443 | HTTPS traffic will be proxied to the container on port 8443. |
80:8080 and 443:8443 because our containers are unprivileged by default, meaning we cannot bind to ports less than 1024 (without additional modification).Volumes
Configure the following volumes:
| Container Directory to Mount | Description |
|---|---|
/config | Directory for Caddy's configuration files (such as Caddyfile or JSON) that must persist for settings to be retained. |
/data | Directory where Caddy stores SSL/TLS certificates and CA information, required for automatic HTTPS to consistently function. |
config and data volumes must have read/write permissions for the www-data user. Caddy will store its configuration and certificates in these volumes (and you want those to persist).Example
Here's an example of directly exposing FrankenPHP to the internet with automatic HTTPS via Let's Encrypt:
services:
php:
image: serversideup/php:8.5-frankenphp
ports:
- 80:8080
- 443:8443
environment:
CADDY_AUTO_HTTPS: "on"
CADDY_HTTPS_SERVER_ADDRESS: "https://example.com"
SSL_MODE: "full"
# Mount the current directory to /var/www/html
volumes:
- .:/var/www/html
- config:/config
- data:/data
volumes:
config:
data:
Use FrankenPHP's Built-in Automatic HTTPS When You Want...
- To run your application and handle SSL termination all in one container
- A simple setup without needing zero-downtime deployments
Bringing Your Own Certificate
If automatic HTTPS isn't an option, you can provide your own certificate from a vendor like ssls.com. Ensure your certificate issuer provides certificates compatible with your web server in PEM format.
To add your own certificate, mount the certificate files to the container:
600 (read/write for owner only). Incorrect permissions will cause errors when loading the private key.services:
php:
image: serversideup/php:8.5-fpm-nginx
ports:
- 80:8080
- 443:8443
environment:
SSL_MODE: "mixed"
SSL_PRIVATE_KEY_FILE: "/etc/ssl/custom/test-key.pem"
SSL_CERTIFICATE_FILE: "/etc/ssl/custom/test.pem"
volumes:
- .:/var/www/html/
- ./certs/:/etc/ssl/custom/
Use Your Own Certificates When You...
- Cannot use Let's Encrypt (corporate policy, network restrictions, etc.)
- Have a specific certificate vendor requirement
- Don't need zero-downtime deployments
Self-Signed Certificate
While browsers will show warnings, self-signed certificates are useful for specific use cases, such as encrypting traffic between containers in a cluster. If you set SSL_MODE to mixed or full without providing a certificate at $SSL_CERTIFICATE_FILE and $SSL_PRIVATE_KEY_FILE, a self-signed certificate will be automatically generated.
services:
php:
image: serversideup/php:8.5-fpm-nginx
ports:
- 80:8080
- 443:8443
environment:
# Set SSL mode to "mixed" (HTTP + HTTPS)
SSL_MODE: "mixed"
volumes:
- .:/var/www/html
The above will generate a self-signed certificate and configure the server to listen on both HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443).
Use a Self-Signed Certificate When You...
- Have a reverse proxy in front of the container handling SSL termination
- Need all traffic to be encrypted (even on the internal network between containers)
SSL_MODE at all. You can configure your reverse proxy to communicate with your PHP container via HTTP (port 8080), eliminating the need to configure SSL within the container.